There was a time when online education was considered a novelty. But now, it has firmly been established as a mainstream and growing industry. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the future of online education promises to be both exciting and transformative.
If you are considering pursuing online education such as a Graduate Certificate of Mental Health with an institution like UTS Online, this article will explore the trends, challenges, and opportunities in the sector to help you better understand where this industry is heading.
Online Education in Australia – Market Size & Forcast
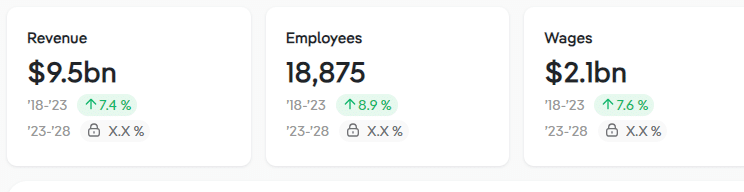
Revenue from online education is projected to experience an annual growth rate of 7.4% over the five-year period spanning 2022 to 2023, reaching an approximate total of $9.5 billion.
The forecast encompasses an anticipated 4.8% increase in the current year, driven by students’ preference for the flexibility and accessibility provided by online learning.
The market share concentration for the Online Education industry in Australia is low, which means the top four companies generate less than 40% of industry revenue.
In Australia, the Education and Training sector maintains an average concentration level of 44%. This figure reflects the proportion of resources, investments, and activities dedicated to education and training within the country.
The sector plays a vital role in shaping the country’s future by equipping its workforce with the necessary skills and knowledge needed for a competitive and innovative global landscape.
How Fast Will Online Education in Australia Grow? Projection
The Online Education market in Australia is poised for a significant shift over the next five years, with a projected decline in its growth trajectory. Over the next five years, the Online Education in Australia market is expected to decline.
How Concentrated Is The Online Education market?
In the realm of Online Education in Australia, market share concentration remains relatively low as of 2023, with the top four companies collectively contributing just 32% of the market’s revenue.
While the overall competition within the industry is not particularly fierce, it is notably more intense among the smaller players in the field suggesting a dynamic landscape where emerging entities have a higher degree of rivalry among themselves.
The Rise of Online Education
Online education, also known as e-learning, has a history dating back to the internet’s early days. In the 1990s, the advent of the World Wide Web paved the way for the development of online courses and virtual classrooms. These early attempts, however, were limited in scope and often struggled to replicate the effectiveness of traditional face-to-face learning.
The real breakthrough for online education came in the 2000s with the proliferation of high-speed internet, multimedia technology, and the development of learning management systems (LMS). Platforms like Blackboard and Moodle provided the infrastructure for institutions to offer online courses to a broader audience.
Still, the early 2000s online education landscape was characterised by asynchronous learning experiences and a lack of interactivity.
Current Landscape
Today, the online education landscape looks significantly different. A combination of factors, including the COVID-19 pandemic, advancements in technology and changing attitudes toward online learning, has led to rapid growth in the industry. A few key factors that have contributed to this growth include:
- Accessibility: The ubiquity of high-speed internet and mobile devices has made online education accessible to a broad demographic. Students no longer need to be physically present on campus to access high-quality education.
- Quality Content: Online courses have evolved to provide high-quality content and interactivity. Multimedia resources, virtual labs and real-time collaboration tools have improved the online learning experience.
- Personalisation: Adaptive learning algorithms and AI-driven platforms allow for personalised learning experiences. Students can progress at their own pace, receive tailored content and access support when needed.
- Global Reach: Online education has a global reach. Students from all over the world can access courses from top institutions without the need to relocate.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Online education can be more cost-effective than traditional classroom-based learning. There are no commuting costs, and often, tuition fees are lower.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the adoption of online education. When schools and universities closed their physical campuses, educators had to adapt to remote teaching quickly. This experience, while challenging, also demonstrated the potential of online education to provide continuity in learning during crises.
Trends Shaping the Future of Online Education
Online education faces an exciting future ahead. Here are some of the trends currently shaping it:
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are revolutionising online education. These technologies enable the development of personalised learning paths, adaptive assessments and intelligent content recommendation systems. AI can track a student’s progress and provide targeted feedback – helping learners stay on track and address their specific needs.
For instance, AI-powered chatbots are now being used to provide instant support to students with common questions. Doing this reduces the workload on instructors and ensures that students receive timely assistance. Additionally, AI is used to analyse student data to identify areas where they can improve course design and content delivery.
2. Gamification and Interactive Learning
Gamification incorporates game elements like points, badges and leaderboards into the learning experience. It is a powerful tool to enhance engagement and motivation in online education. Gamified elements make learning more interactive and enjoyable, which can be especially effective for K-12 students and adult learners.
Furthermore, interactive learning experiences like virtual labs, simulations and collaborative projects are becoming more prevalent in online courses. These activities provide hands-on experiences and practical skills development, mirroring the benefits of traditional, in-person education.
3. Microlearning
Microlearning is a trend that involves breaking down educational content into small, easily digestible units. These bite-sized lessons are designed to be completed in a short amount of time, making them ideal for busy individuals.
Microlearning is particularly effective in professional development and corporate training, where employees can quickly acquire specific skills or knowledge without disrupting their work schedules.
4. Augmented and Virtual Reality
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are poised to impact the future of online education significantly. AR and VR technologies provide immersive and interactive learning experiences that can simulate real-world situations. Here’s how they are currently being used in online education:
Virtual Labs: In science and engineering disciplines, students can conduct experiments in virtual laboratories. They can manipulate objects, observe chemical reactions, and explore complex concepts in a safe and controlled environment.
Field Trips: AR and VR allow students to take virtual field trips to historical sites, museums, or even distant planets. These experiences can bring history, geography, and science to life in a way that traditional textbooks cannot.
Language Learning: Language learners can immerse themselves in virtual environments surrounded by native speakers, helping them develop conversational skills.
Medical Training: Medical students can practise surgical procedures in a realistic virtual environment before ever touching a patient.
While the adoption of AR and VR in education is still in its early stages, it holds immense potential for revolutionising how students learn and experience subjects.
5. Competency-Based Education
Competency-based education (CBE) is an approach that focuses on what students know and can do rather than the time spent in a classroom. In a CBE model, students progress when they demonstrate mastery of a particular skill or knowledge area. This approach allows students to move at their own pace and is often more affordable and flexible than traditional models.
CBE is particularly popular in workforce development and vocational training, enabling learners to acquire job-relevant skills efficiently. This model also aligns well with online education, as it relies on clearly defined competencies and assessments they can administer digitally.
6. Social Learning and Collaboration
One criticism of online education is the perceived lack of social interaction and collaboration students get in traditional classrooms. However, modern online education platforms increasingly incorporate social and collaborative elements to address this concern.
Online discussion forums, group projects, and peer-to-peer feedback systems are now standard features in many online courses. These tools encourage interaction and the exchange of ideas among students, mirroring the collaborative nature of traditional education.
Moreover, social learning platforms, like Slack and Microsoft Teams, are integrated into online courses, providing students with opportunities to interact, share resources, and engage in discussions with their peers.
7. Blockchain Credentials
Blockchain technology is being explored as a way to secure and verify educational credentials. Academic certificates, diplomas, and degrees can be stored on a blockchain, making them tamper-proof and easily shareable. This innovation streamlines the process of verifying qualifications for both employers and educational institutions.
Blockchain also opens up the possibility of micro-credentials, where students earn badges or certificates for specific skills or achievements within a course. These can be valuable for job seekers and employers looking for targeted expertise.
8. Remote Proctoring and Security
The growth of online education has given rise to concerns about academic integrity and cheating. However, online proctoring services have been developed to address this.
These services use webcams and AI to monitor students during exams, ensuring they are not using unauthorised resources or receiving outside help.
While remote proctoring has received some controversy due to privacy concerns, it is an area that continues to evolve. Striking the right balance between maintaining academic integrity and respecting students’ privacy is a challenge the industry is working to address.
Challenges in the Future of Online Education
As online education continues to evolve, several challenges must be navigated to ensure its success and accessibility:
1. The Digital Divide
As not everyone has equal access to technology and the internet, the digital divide is a significant challenge in online education. Subsequently, bridging this gap is essential to ensure that all students have equitable access to learning resources.
Efforts to address this issue include providing devices and internet access to underserved communities and developing curriculum materials that students can access offline.
2. Quality Assurance
Ensuring the quality of online education is essential. Not all online courses are created equal, and a wide disparity between content and delivery can exist. Therefore, standardised quality assurance measures, accreditation, and learner feedback systems are needed to maintain educational standards.
In addition, there is a need for ongoing teacher training and professional development to equip educators with the skills and knowledge to deliver online instruction effectively.
3. Student Engagement and Motivation
Maintaining student engagement and motivation in online courses can be a challenge. Without the structure of a physical classroom, some students may struggle to stay on track.
To combat this, educators must employ effective pedagogical strategies and technology to create interactive and engaging learning experiences.
4. Data Privacy and Security
Online education platforms collect a wealth of student data, which they must handle securely and responsibly.
Some data privacy concerns have arisen, particularly with the increased use of AI and proctoring technologies. Subsequently, protecting students’ data while still using it to enhance learning is a delicate balance that educational institutions must strike.
5. Inclusivity and Accessibility
Online education should be accessible to all, including individuals with disabilities.
Consequently, ensuring that course materials are compatible with screen readers, providing video transcripts, and implementing other accessibility features are essential to supporting a diverse student population.
Opportunities in the Future of Online Education
Without doubt, the future of online education is bright and it presents numerous opportunities:
1. Lifelong Learning
In today’s rapidly evolving job market, the need for lifelong learning is more significant than ever.
Online education provides a flexible and accessible way for individuals to acquire new skills and knowledge continually, making career transitions and upskilling more attainable.
2. Global Learning
Online education is inherently global. Students from around the world can enrol in courses from top institutions without the need for international relocation.
As a result, this opens up cross-cultural collaboration and learning opportunities, fostering a global perspective.
3. Cost-Effective Education
Online education often costs less than traditional, on-campus education. Reduced overhead costs – like maintaining physical infrastructure – can translate to lower tuition fees. This affordability makes higher education more accessible to a broader range of learners.
4. Customisation and Personalisation
AI-driven platforms enable customised learning experiences.
Students can receive personalised recommendations, support and pacing, allowing them to focus on areas where they need the most help.
5. Innovation and Experimentation
The online education landscape is highly dynamic – giving institutions and educators the freedom to experiment with new teaching methods, technologies and approaches.
This environment fosters innovation and the development of cutting-edge educational tools and resources.
Conclusion
Online education has come a long way since its inception in the early days of the Internet. Today, it is a vibrant and growing industry with a promising future.
The ongoing development of technology, combined with innovative teaching practices, is set to transform the way we learn and access education.
While online education faces challenges, such as the digital divide and ensuring data privacy, the opportunities it offers, including lifelong learning, global accessibility, cost-effectiveness, customisation, and innovation, outweigh these challenges.
As we move forward, the future of online education will likely involve a fusion of technology and pedagogy, creating a rich and interactive learning experience for students of all ages and backgrounds.
With the right investments, policies and innovation, online education has the potential to redefine how we think about education – making it more inclusive and accessible for all.







