SSL Certificates are small pieces of information that allow a website to be verified by major browsers. SSL stands for ‘Secure Socket Layer’. It is used on Web servers to create a trustworthy virtual connection between your web server and the Web browser you are trying to access. SSL Certificates is used in making transactions over the Internet such as making online purchases, receiving e-mail messages and conducting business on the Internet..
SSL Certificates are usually issued with a domain name, specifying the type of certificate, the issuer and also the expiration date. It is possible to obtain multiple SSL Certificates for different purposes. For instance, you may need to verify a domain name before giving it to a customer. Similarly, multiple certificates can help in assuring that the same website is not published on different sites. Multiple SSL Certificates can also be required for various Ecommerce applications. For instance, when buying products from an online store, multiple certificates will ensure that the order details are encrypted and cannot be copied and used on another site.
To start, you should purchase a SSL Certificate from a trusted provider, usually a web developer or a Web hosting company. The certificate contains an encoded string of numbers which needs to be converted into a string of characters. This is done by the server, which authenticates the message, checks it against all the websites that use the same port number. The result is an SSL Certificate which contains the digital fingerprint of the server, which guarantees authenticity. In the first step, the issuer verifies the certificate and, in the second step, the browser checks the authenticity of the certificate.
If authenticity is verified and the browser successfully verifies the authenticity of the certificate, the user is prompted to enter the website that he wants to visit, a domain name or IP address. A ‘ok’ message is displayed in the browser window, and the browser sends an error message to the trusted certificate authorities, which in turn reply back to the browser. The browser then follows the pathname which is contained in the response.
If the browser received an error message, it indicates that there is some problem in the way the request was made between the browser and the web server. It may be due to various reasons like poor infrastructure, server problems or network issues. The user will have to contact the company offering the SSL Certificates service and get his certificate decrypted. It usually takes one hour or so.
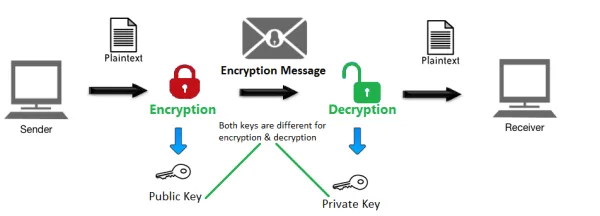
The entire process of SSL Certificates uses public key cryptography. With public key cryptography, the owner of the certificate can create many different identities with different passwords. Anyone can encrypt a web page, send it to the web server will decrypt the page before forwarding it to the users. As the protocol does not allow any unauthorized access to the private keys, ssl certificates use a lot of work arounds to ensure that the owners of the SSL Certificates can make sure that only they can make access to their passwords.
Transport Layer Security
Transport Layer Security (TLS), the successor to SSL now-obsolete Secure Sockets Layer, has been designed to offer strong encryption and authentication over a public-and-private network as part of an advanced security system. By encrypting the details of a communication in transit, this technology ensures that only authorized parties have access to the data that is being sent or received over the network. The primary protocol for providing this protection is the Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Transport Layer Protection (TLP). A standardised format called the Elliptical Signature algorithm is used to verify the identity of the sender of the message, preventing the disclosure of sensitive information such as the contents of a message or the IP address of a computer.
An encryption system called Transport Layer Security (TLS) is used to protect the details of a confidential communication, ensuring that only the intended recipient can read it. For instance, the web browser can be set to automatically encrypt all web pages before sending them across the Internet, although not all browsers support this feature. Most commercial browsers have implemented some form of TLS, although several open source projects are also in operation. The main advantage of TLS is that it provides an advanced level of security for confidential or protected data. As an encryption mechanism, it makes possible the transmission of signed messages, ensuring that only the intended recipient can read them.
While TLS is an important step towards preventing unauthorized access to data on the Internet, it is only one part of a comprehensive security suite. Encryption and authentication may be applied to the network layer, the service layer, or both. The advantage of applying both is that they prevent attackers from observing traffic on the Internet and attacking application servers, which are critical to the efficient operation of any organization. Attacks against application servers are especially troublesome because they usually do not require knowledge of the inner workings of the application server, as is often the case. In addition, combining both transport layer security and application-layer security is sometimes more effective than just applying these two methods individually.
Certificate Authority
In computer security and in the electronic age, there has been a major shift towards issuance of CA certificates, also known as trusted root certificates, to authenticate the identity of servers and other entities. In computer security, a CA is an organisation that issues digital keys called certificates to establish trust between servers and other entities. A digital certificate validates the authenticity of a given key by the name of the certificate holder. The most common use for CA certificates is as signatories for Ecommerce transactions on the Internet. In the electronic age, it is very easy for end-users to check whether a website they are visiting is authenticated or not.
The Certificate Authority is a private key organization that issues digital certificates for specific websites. This entity may be a web designer that requests the CA certificate for a specific web site, or it could be any entity that has valid reasons to trust the CA. Once a user types in a website address in the web browser, it will first look through the CA list to see if it finds a matching digital certificate for that website.
If it finds one, the CA then search its database of digital certificates issued by other entities. If it finds one that matches, then it will display the matching details in its website. However, if it does not find a match, it will return a message indicating that there were no matching certificates found. Therefore, the CA is the only entity that can successfully match the signature on the virtual certificate so that the end-user can verify the authenticity of the website. Hence, it becomes important that the CA is chosen carefully when you want to get your site hosted over the Internet.
Best SSL Providers
Below are our selectd best SSL certificate providers of 2021:
Summing up
SSL certificates allow users to validate the identity of websites they visit. They provide system security and facilitate the transfer of sensitive information on the Web.







