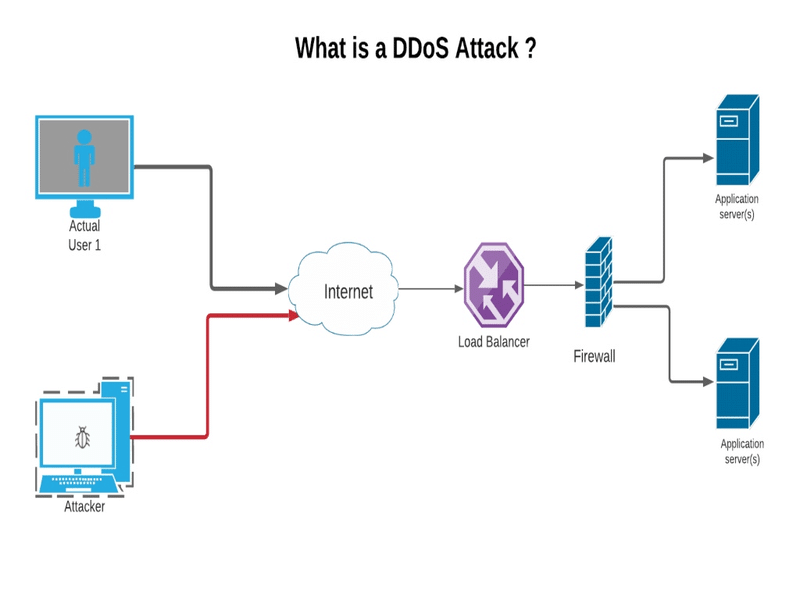
A distributed denial-of-service, or DDoS, attack is basically one of the strongest weapons online. When you read about a site being attacked by hackers, it usually means that it has been a victim of a successful DDoS attack. Basically, in a DDoS, attackers have tried to effectively bring down a server by flooding it with too much active Internet traffic.
his is a common method used in the attack against government and corporate networks. The way it works is simple: attackers create a large number of bogus Web sites, which are all synchronized with each other, and they all use common programs like the WordPress blog service to post entries and data.
There are different types of DDoS attacks that can be attributed to the WordPress software. These different types are application-layer attacks, application protocol attacks, and cross-site scripting. Each of these has several components that contribute to the seriousness of a DDoS. Let’s take a look at each of these and explore the possible ways they can affect you.
Application-layer attacks occur when attackers try to compromise the security of your servers by exposing sensitive information. An example would be SQL injection, where an attacker can insert malicious code into your server’s database.
Similarly, an application protocol attack can involve the use of scripts to send fake messages to other devices on your network. Cross-site scripting, which refers to an attack on another web server based on content that originates from a specific site, can also cause DDoS attacks.
In order to prevent a DDoS from hitting your business, it’s important to understand the nature of cyber criminals and the methods they use to infiltrate your system. Cyber criminals typically utilise several techniques. Some of these include password cracking, automated scanning, DoS attacks, and denial of service (DoS) attacks.
In order to prevent any of these attacks from happening, it’s important to have your system protected by a reliable provider. There are many DDoS protection providers in the market but only a few of them are highly reliable and effective.
Targeting WordPress. A Content Management System
WordPress is a popular CMS used by millions of users around the world. Because it’s easy to install and use, it attracts a lot of hackers and scammers who want to gain access to your database and other important areas.
Because WordPress is used by everyone, it’s also vulnerable to attackers who use downtime or network troubles to overload your server. When this happens, the WordPress system becomes the cyber criminal’s first victim. Many attacks occur during normal everyday activities such as updating WordPress, adding new plugins, or editing a post.
During DDoS attacks, the attacker overloads your server with traffic. Different types of attacks include POP/SMTP floods, TCP flooding, and buffer overflows. An example of a DDoS is when hundreds of thousands of requests are sent to the same server at the same time. In order to prevent such attacks, your system should have several different layers of protection.
Common DDoS Attack Types.
- ICMP (Ping) Flood.
- SYN Flood.
- Ping of Death.
- Slowloris.
- NTP Amplification.
- HTTP Flood.
- Zero-day DDoS Attacks.
- Volume Based Attacks
DDoS Mitigation
DDoS mitigation refers to a group of computer-networking security measures and/or methods for mitigating or protecting the adverse impact of multiple distributed denial-of-Service attacks (DDoS) on networks attached to the Internet.
These attacks result in a catastrophic reduction in network performance due to excessive network resource consumption, unreliable or slow Internet connection, and other adverse impacts. An attack can have numerous consequences depending on its nature and the geographical area targeted.
DDoS mitigation requires a comprehensive plan that will prevent or mitigate the adverse impact of attacks based on a detailed analysis of the targeted network size, infrastructure, and operation.
The mitigation process begins by blocking the attacker’s access to the Internet, preventing him or her from sending packets of targeted data or information to its destination.
This blockage is typically provided by one or more network blocklists, IP filters, or security servers. Once this protection has been put in place, a DDoS mitigation strategy can be initiated to deal with the remaining effects of the attack.
Today, there are several modern DDoS attack techniques that are making it increasingly difficult for attackers to target smaller network sizes and more geographically distant locations.
For example, a DDoS can take down a medium-sized company’s IT systems, but a group of young hackers with limited experience attacking the same target can easily overcome any measure in place to protect the bigger corporate entity.
In addition, DDoS mitigation has become more advanced, using prevention and protection against specific types of attacks rather than blocking all Internet traffic as was often the case in the past.
While blocking all Internet traffic is still a very real possibility for a large company or an international government, today’s modern techniques allow for the more subtle usage of various techniques against specific IP addresses or networks of IP addresses.
Summary
The perpetrators of denial of service attacks attempt to make a machine or network resource inaccessible to intended users, either temporarily or indefinitely by disrupting the services of an Internet-connected host.
Typically, this is achieved by flooding the target machine or resource with redundant requests to overload the system and prevent some or all legitimate requests from being fulfilled.
A Distributed Denial-of-Service attack occurs when multiple systems invade the bandwidth or resources of a targeted system, often from thousands of malware-infected hosts.
Since the inbound traffic flooding the victim comes from different sources, it becomes difficult to distinguish legitimate user traffic from attack traffic, especially when it is spread across multiple points of origin.







