Latest analytics predicted IoT devices will see increasing growth by 18% to 14.4 billion from 2023 to 2024, and by 2025, this could increase to 27 billion connected IoT devices. One of the trends in 2023 that will enable this growth is the increased replacement of 2G/3G wireless networks with 4G/5G networks.
By seamlessly merging the physical and digital realms, IoT has the potential to enhance efficiency, convenience, and insights across various domains, revolutionising how we interact with our environment and harness data-driven decision-making.
However, as this intricate web of connectivity grows, it also brings to the fore challenges related to security, privacy, and the responsible management of the vast amounts of data generated.
As IoT continues to evolve, its impact on industries, homes, and society at large is undeniable, shaping a future where interconnectedness and intelligence converge to reshape the way we live and work.
What is IoT (Internet of Things)?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of physical objects, gadgets, cars, buildings, and other things that are equipped with connectivity, software, and sensors to collect and exchange data online.
These things’ ability to connect with one another and with people thanks to the IoT opens up possibilities for automation, optimisation, and new services.
Smart household appliances, wearable fitness trackers, self-driving automobiles, and industrial sensors are a few examples of IoT gadgets. IoT has a wide range of possible uses, including enhancing energy efficiency, transportation, and many other industries.
Topics covered in this article.
1. How does IoT work?
2. The applications of IoT
3. Why dies IoT matter and how it can improve your life?
4. What is IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things)?
5. What are some of the challenges in IoT?
6. What are some of the risks of IoT?
1. How does IoT – The (Internet of Things) work?
IoT works by connecting physical devices, sensors, and objects to the internet, allowing them to send and receive data. These devices are embedded with sensors, software, and communication technology that allow them to communicate with each other and with the internet.
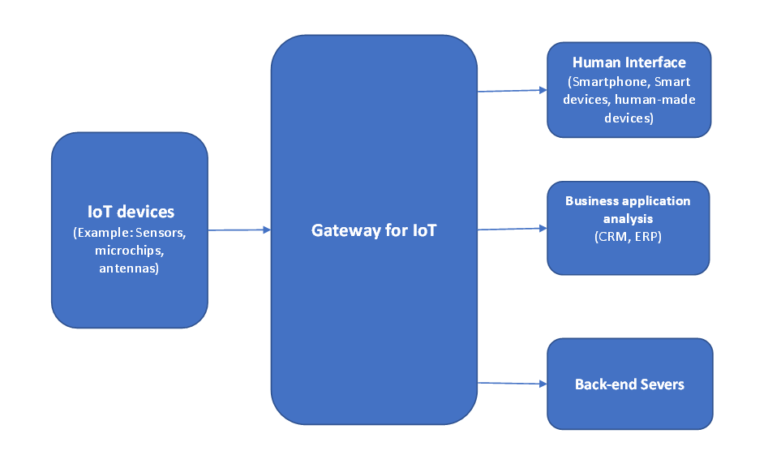
Once connected, Internet of Things (IoT) devices have the capacity to collect environmental data, encompassing factors like temperature, humidity, and location. The data is then transmitted to a central system for comprehensive analysis, enabling the initiation of subsequent actions, such as activating a light source or regulating temperature settings.
Addtionally, these IoT devices possess the capability to receive directives from a central system, often facilitated through a user’s smartphone. A prime example includes a user employing their smartphone to illuminate a smart light bulb or unlock a smart lock, showcasing the responsiveness inherent in IoT applications.
The functioning of IoT hinges on a diverse range of technologies including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks, which facilitate the connection of devices to the internet. This framework also heavily relies on cloud computing and advanced analytics for the storage and processing of the copious amounts of data generated by IoT devices.
2. IoT Applications (Internet of Things)
The Internet of Things (IoT) boasts a vast spectrum of applications that span across numerous industries and diverse use cases.
This interconnected network of physical devices, vehicles, buildings, and other items embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity capabilities has revolutionized the way industries operate and has transformed everyday life.
From manufacturing and healthcare to agriculture and smart cities, IoT technologies are driving innovation, efficiency, and convenience in unprecedented ways. Here are some examples of IoT applications:
Smart homes – IoT devices can be used to automate and control home appliances and systems, such as smart thermostats, smart lighting, and security systems.
Wearables – IoT devices can be worn on the body to track fitness and health, such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, and medical devices.
Industrial automation – IoT devices can be used in manufacturing and industrial settings to optimize processes, reduce downtime, and improve efficiency.
Agriculture – IoT devices can be used in farming and agriculture to monitor soil quality, crop growth, and weather patterns, as well as optimize water and fertilizer usage.
Smart cities – IoT devices can be used to monitor and manage city infrastructure and services, such as traffic monitoring systems and smart parking meters.
Healthcare – IoT devices can be used in healthcare settings to monitor patient health, deliver medication, and improve patient outcomes.
Transportation – IoT devices can be used to track and monitor vehicles, optimize routes and schedules, and improve safety.
Energy management – IoT devices can be used to monitor energy usage, optimize energy consumption, and reduce waste.
IoT has numerous applications across various industries and use cases, offering the potential to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance business productivity.
3. Why Does IoT matter and how IoT can improve our life?
IoT can improve our lives in many ways, both big and small. Here are some examples of how IoT can make a positive impact:
Health and wellness – Wearable fitness trackers and medical devices can help individuals monitor their health and make informed decisions about their lifestyle.
Home automation – Smart home devices can help automate tasks, such as turning off lights and adjusting thermostats, to save energy and make our lives more convenient.
Safety and security – IoT devices can be used to monitor homes and environments for potential hazards, such as smoke detectors and security cameras.
Transportation – Connected cars and smart traffic systems can help reduce traffic congestion and accidents, making our commutes safer and more efficient.
Environmental sustainability – IoT devices can be used to monitor and reduce energy usage, optimize water consumption, and improve waste management.
Accessibility – IoT devices can provide greater accessibility for people with disabilities, such as smart home devices that can be controlled by voice commands.
Personalisation – IoT devices can learn and adapt to our preferences and behaviors, providing personalised experiences and making our lives more comfortable and enjoyable.
IoT matters because it has the potential to improve our lives and transform industries in many ways.
4. What is IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things)?
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is the term used to describe the application of IoT technology in several industrial sectors, including manufacturing, energy, transportation, and agriculture.
IIoT gathers and analyses data from industrial processes and equipment using sensors, hardware, and software. Then, with the use of this information, operations can be improved, efficiency increased, expenses decreased, and safety increased.
For example, in a manufacturing plant, IIoT sensors can be used to monitor equipment performance and detect issues before they lead to downtime or breakdowns.
In the energy sector, IIoT devices can be used to monitor power usage and optimize energy consumption. In transportation, IIoT technology can be used to track and monitor vehicles, as well as optimize routes and schedules.
IIoT has the potential to revolutionize industrial processes and improve overall productivity and profitability. By leveraging real-time data and analytics, IIoT can help companies identify opportunities for improvement and make data-driven decisions.
5. What are some the challenges in IoT?
While the Internet of Things (IoT) presents a plethora of advantages, it is not without its share of hurdles and complexities. Navigating through these challenges is crucial for realising the full potential of IoT technology. Here, we highlight some of the pivotal challenges that the realm of IoT encounters:
- Security – IoT devices often lack adequate security measures, making them vulnerable to cyber attacks and data breaches.
- Privacy – IoT devices collecting and using personal data can raise privacy concerns, particularly if the data is used without the user’s knowledge or consent.
- Interoperability – IoT devices are often developed by different manufacturers and may use different protocols and standards, making it difficult for them to work together seamlessly.
- Scalability – As the number of connected devices grows, managing and scaling IoT systems becomes increasingly complex and challenging.
- Power and energy – Many IoT devices are battery-powered, which can limit their functionality and lifespan. Energy-efficient solutions are needed to address this challenge.
- Data management – The massive amount of data generated by IoT devices can be difficult to manage and analyze, requiring advanced data management and analytics tools.
- Cost of devices – IoT devices can be expensive to develop and deploy, making it challenging for smaller companies and organizations to adopt IoT solutions.
Addressing these challenges will require collaboration between industry, government, and academia to develop and implement best practices and standards for IoT security, privacy, and interoperability.
6. What are some of the risks of IoT?
Interoperability – IoT devices from different manufacturers may use different protocols and standards, making it difficult for them to work together seamlessly and posing compatibility risks.
Complexity – The complexity of IoT systems can make them challenging to manage and secure, requiring specialised skills and expertise.
Legal and regulatory – The rapid growth of IoT has outpaced the development of legal and regulatory frameworks to govern its use, raising issues around liability, accountability, and consumer protection.
To reduce these risks, organisations and individuals must implement best practices for IoT security, privacy, and safety. This includes using strong passwords, encrypting data, keeping software up to date, and regularly auditing IoT systems.
It also requires collaboration between industry and government to develop and implement standards and regulations to ensure the safe and responsible use of IoT.
IoT Revenue & Market Growth
The IoT industry is expected to be worth over $1 trillion by 2024 (Global Data) IoT market in 2022 is currently worth an approximate of $800 billion. It is expected to grow atleast $1 trillion at a 13% CAGR in 2024.
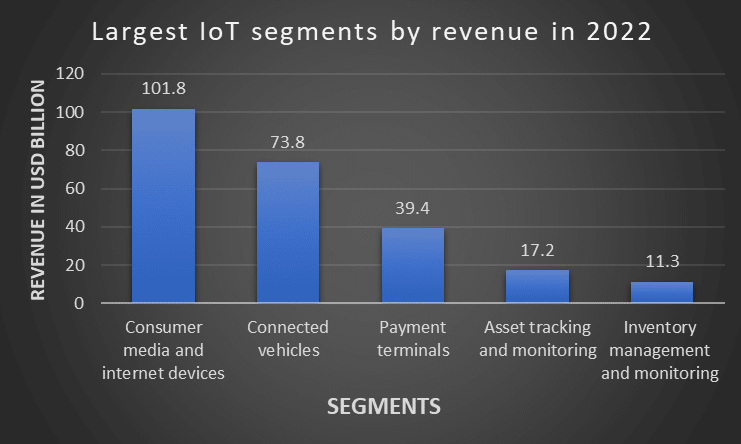
Below are the top segments which contributed in IoT by revenue in 2022 where Consumer media topped $100 billion of revenue in 2022
List Of Top – The Internet Of Things (IoT) Companies
Below are some of the most popular IoT Software Solutions and Services Companies worldwide.
- iTechArt (New York, US)
- Oxagile (New York, US)
- SumatoSoft (USA & Europe)
- Innowise Group (Warsaw, Poland)
- Style Lab IoT Software Company (San Francisco, CA)
- HQ Software Industrial IoT Company (USA & Europe)
- PTC (Boston, Massachusetts)
- Cisco (San Jose, CA)
- ARM IoT Security Company (Cambridge, Cambs)
- Huawei (Shenzhen, Guangdong)
- GE Digital (San Ramon, California)
- Bosch IoT Sensor Company (Farmington Hills, MI)
- SAP (Walldorf, Germany)
- Siemens IoT Analytics Company (Berlin and Munich, Germany)
- IBM (New York, U.S.)
- Andersen Inc. (New York, U.S.)
- ScienceSoft (USA & Europe)
- DICEUS (USA & Europe)
Top Growth Opportunities for IoT in 2024
In the realm of the Internet of Things (IoT), the present landscape and upcoming developments are noteworthy.
- Current IoT Landscape
As per Frost & Sullivan’s estimations, the global count of IoT devices reached a staggering 35.37 billion in 2022. Notably, more than 51% of these connections were dedicated to applications in building automation, security, and surveillance.
The remaining connections were dispersed across various sectors, encompassing factory automation, industrial applications, portable asset tracking, and fixed-asset monitoring.
- Anticipating IoT Growth (Beyond 2023-2024):
In 2023, a projection of 41.76 billion active IoT-connected devices worldwide has been established. This envisaged surge signals an 18% increase in connections compared to the previous year. Frost & Sullivan’s insights point toward several significant factors propelling this growth.
These factors encompass the swift advancement of automation processes, persistent corporate digital transformation initiatives, the recuperation of value chains following the economic aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic, and the widespread deployment of 5G connectivity networks.
- Prominent Applications Driving IoT Adoption:
In the expansive IoT landscape, security and surveillance applications are asserting their dominance. Notably, IT decision-makers on a global scale are increasingly embracing IoT technologies to fortify security measures aimed at safeguarding critical assets across diverse industries.
The implementation of IoT-driven intelligent security systems holds the promise of enhancing safety by identifying individuals and objects entering and exiting buildings. Additionally, these systems monitor facility status and efficiently transmit security alerts and emergency responses.
Moreover, the integration of edge computing and artificial intelligence (AI) is swiftly becoming indispensable for surveillance systems. This integration facilitates real-time image monitoring and streamlined data processing, augmenting the effectiveness of surveillance endeavors.
- IoT’s Varied Impact Across Industries:
In the year 2023, the adoption of industrial IoT strategies and solutions will gather momentum, aimed at optimising operations, boosting productivity, elevating product quality, and curbing expenses within organisations.
Simultaneously, the ascent of digital twins within the Industry 4.0 framework will be fueled by data analytics and IoT technologies, enabling applications like predictive maintenance and fault identification.
- Driving Innovation in Industrial Automation:
IoT’s influence extends to automating manual processes while also enriching customer experiences. For instance, electric vehicles equipped with advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) will respond automatically through IoT triggers, enhancing overall safety.
This landscape incorporates emerging technologies like 5G, edge computing, and smart tire sensors, which work collaboratively to detect risks and prevent collisions.
IoT’s Role in Immersive Experiences:
As the demand for immersive encounters escalates, technology providers are set to explore new revenue avenues with IoT expected to reach $2.2 Billion by 2028.
The year 2023 will witness a heightened requirement for 5G networks and edge computing to empower dynamic augmented reality (AR) and mixed reality (MR) experiences with ultra-low latency. Industries like education are embracing these technologies for novel applications.
In the metaverse domain, IoT’s significance comes to the fore, enabling interaction between the real and virtual worlds. This necessitates IoT providers to gear up with software, sensors, and devices tailored for metaverse integration, thereby contributing to a more immersive reality.
- Frontiers of Innovation with Multi-Access Edge Computing:
The global multi-access edge computing (MEC) market is on an upward trajectory as telecom operators and cloud providers deploy commercial services at scale. The synergy of 5G and MEC reduces latency and increases capacity, positioning computing power closer to end-users for novel applications.
Projections indicate that edge computing will generate $3.71 billion in revenue between 2023 and 2024, marking a remarkable 172% growth from the preceding year. This is spurred by the demand for local data storage and real-time processing, crucial for latency-sensitive applications like AR, MR, extended reality (XR), digital twins (DT), and autonomous vehicles.
IoT Trends Across Industries:
In 2023, IoT’s reach extends to promoting sustainability, facilitating digital payments, and driving growth in low-power wide-area networks (LPWANs).
CEOs harness connected devices to gather and analyse data on environmental factors, fostering eco-conscious business practices. Moreover, IoT sensors remotely monitor various operational and environmental parameters, spanning traffic flow, pollution levels, energy consumption, and more.
Industries such as utilities, agriculture, and supply chains embrace large-scale IoT projects bolstered by LPWANs. In the evolving IoT landscape of 2024 and beyond, a synergistic approach emerges, combining LPWAN technologies (cellular and proprietary) with other IoT solutions, including satellite connectivity, fostering innovative and holistic solutions.
10 Top IoT Trends For 2024
Here are 10 Top IoT (Internet of Things) trends that have been prominent and continue to shape the landscape:
- Edge Computing: IoT devices are generating vast amounts of data, and edge computing involves processing this data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving real-time decision-making.
- 5G Integration: The rollout of 5G networks enables faster and more reliable communication between IoT devices, unlocking new possibilities for applications that require high bandwidth and low latency.
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: AI and ML are being integrated into IoT systems to analyze and interpret data, enabling predictive maintenance, anomaly detection, and more advanced automation.
- Security Enhancements: As the number of connected devices grows, so does the potential attack surface. IoT security is evolving with features like device authentication, encryption, and secure firmware updates.
- Smart Cities: The concept of smart cities involves using IoT to manage urban services more efficiently, such as traffic control, waste management, energy consumption, and public safety.
- Healthcare IoT: IoT is transforming healthcare with applications like remote patient monitoring, wearable health devices, and smart medical equipment for improved patient care and management.
- Industrial IoT (IIoT): In industries like manufacturing, IIoT is being used for predictive maintenance, supply chain optimization, and overall operational efficiency improvements.
- Environmental Monitoring: IoT devices are being deployed for environmental monitoring, helping to track pollution levels, climate changes, and wildlife conservation efforts.
- Retail and Customer Experience: IoT is enhancing retail through connected shelves, personalised shopping experiences, and improved inventory management.
- Agriculture IoT (AgriTech): IoT is revolutionising agriculture with precision farming techniques, where sensors and data analysis optimise crop yield, manage irrigation, and monitor livestock.
The Transformative Impact of IoT On Businesses
Few innovations have left a profound an impact on businesses IoT. The result has been a paradigm shift, redefining business operations across industries and offering unprecedented opportunities for growth, efficiency, and innovation.
- Enhanced Data-driven Decision Making
At the heart of IoT’s influence on businesses lies its ability to generate copious amounts of real-time data. This treasure trove of information enables companies to make more informed and timely decisions.
By collecting data from various sources such as customer behaviors, production processes, and supply chain logistics, businesses can gain insights that were previously inaccessible.
- Operational Efficiency and Cost Savings
IoT’s integration into business processes has streamlined operations and ushered in new levels of efficiency. Connected devices allow for remote monitoring and predictive maintenance of machinery, reducing downtime and minimising maintenance costs.
Manufacturing plants equipped with IoT sensors can optimize production by identifying bottlenecks in real-time and adjusting workflows accordingly.
- Personalised Customer Experiences
IoT has redefined customer engagement by enabling businesses to offer tailored experiences. With data gathered from connected devices, companies can better understand their customers’ preferences and behaviors, leading to personalised recommendations and offerings
- Supply Chain Management and Logistics
IoT has revolutionized supply chain management, allowing companies to monitor the movement of goods throughout the entire logistics process. Sensors embedded in shipments provide real-time updates on location, temperature, humidity, and other critical variables.
The data not only enhances transparency but also enables swift interventions in case of deviations from the desired conditions, safeguarding the quality of products in transit.
- New Business Models and Revenue Streams
The advent of IoT has opened doors to novel business models and revenue streams. Companies can now offer their products as services, capitalizing on IoT’s capabilities.
For instance, instead of selling a product outright, manufacturers can provide it as a service, charging customers based on usage. The shift to a subscription-based model fosters long-term relationships with clients and generates recurring revenue.
The Trajectory of IoT Adoption
As we cast our gaze forward, the path of IoT adoption stretches ahead with unwavering promise. Forecasts from experts illuminate a compelling vision: the year 2025 is poised to witness a staggering surge, surpassing a monumental milestone of 25 billion active IoT endpoints.
This numerical testament underscores the imminent reality of a world that is not just connected, but profoundly data-centric, revolutionising the way we interact with technology and the environment around us.
Yet, this journey of evolution remains far from static. The future of IoT is poised to be interlaced with remarkable advancements in complementary technologies, fueling an exponential growth trajectory.
The symphony of these technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI), edge computing, and blockchain, is set to amplify the potential of IoT in unprecedented ways.
The Road Ahead For IoT
The journey of IoT in the business world is far from over. As technology continues to evolve, businesses will need to adapt, innovate, and collaborate to harness IoT’s potential fully.
Governments and regulatory bodies will play a role in establishing frameworks that ensure data privacy and security while encouraging innovation.
Overall, the future of IoT looks very promising, brimming with substantial prospects for fostering innovation, fostering economic expansion, and bestowing noteworthy social advantages.
Nonetheless, it is imperative to recognise that the road ahead is not devoid of obstacles. Effectively grappling with the multifaceted challenges and potential risks intertwined with the IoT landscape will undoubtedly emerge as a pivotal determinant in shaping the trajectory of this technology.
By proactively addressing issues such as data privacy, cybersecurity vulnerabilities, interoperability hurdles, and the ethical implications of widespread connectivity, we can pave the way for a future where IoT stands as a testament to safe, conscientious, and advantageous technological advancement.
In the ongoing evolution towards interconnected cities, the prevalence of digital payments is poised to surge, with IoT taking center stage in this transformation.
The expansion of IoT-based payments, encompassing transactions facilitated by internet-connected devices operating with a degree of autonomy, is set to span a multitude of industry domains.
The adoption of digital advancements, such as IoT sensors, AI algorithms, visual computing, machine learning (ML), and networking solutions, will witness a notable rise.
Retailers will increasingly integrate contactless technologies, self-checkout systems, and even cashierless setups, driving the popularity of these digital technologies further.
As companies continue to embrace and invest in IoT, they position themselves at the forefront of a new era of connectivity and efficiency. The future promises exciting possibilities as IoT reshapes industries and propels businesses toward unparalleled growth and success.







