Utilising bots as their weapons of choice, these threat actors quietly target the APIs, websites, and applications that power these automations. Their objective: to corrupt business logic on a massive scale. In doing so, they siphon revenues, exploit sensitive data on an unprecedented scale, tarnish reputations, impair website performance, and inflate technical costs.
Comparable to the early days of ransomware, this seemingly innocuous risk, initially impacting consumers, is stealthily crossing over into the enterprise realm,
Unlike ransomware, which delivers explosive impacts, malicious bot automation’s effect on corporate value is insidious but equally pernicious.
This pervasive problem prompted our research, one of the largest analyses of its kind. Our aim is to quantify the scale of this issue, providing businesses with insights into the magnitude of value lost due to malicious automation.
Malicious bot automation is more than a nuisance; it is a corrosive force that erodes corporate value, one automated action at a time. .
Recent attacks have shed light on the origins of malicious automation, with the majority of such threats traced back to Russia and China. These cyber adversaries have honed their skills in deploying automated bots to exploit vulnerabilities in business infrastructures.
The consequences are profound, with the annual cost of combating these malicious bots averaging a staggering $85.6 million per company, per year.
This amount far surpasses the average ransomware payment of $1.5 million, making it one of the costliest cyber threats faced by businesses today and equivalent to the eighth-largest GDPR fine ever issued.
What is particularly concerning is the persistent disparity in detection times. While threats breaching the internal perimeter are typically identified within two weeks, malicious automated attacks often remain undetected for an average of four months.
The lengthy window of vulnerability allows threat actors to wreak havoc, bleed revenues, and compromise sensitive data unchecked, resulting in severe financial and reputational damage to businesses.
The emergence of Russia and China as prominent sources of malicious automation underscores the need for vigilant cybersecurity measures. Businesses must prioritise the identification and mitigation of these threats to safeguard their operations, finances, and data.
Attack Origin Locations
Cybersecurity experts says 53% of all cyberattacks have been traced back to Russia or China, highlighting the significance of these countries in the evolving cybersecurity landscape.
A Closer Look at the Numbers
- 72% from China: A staggering 72% of organisations surveyed reported being targeted by cyber threats originating in China. These threats encompass a wide range of attack vectors, posing significant challenges to businesses worldwide.
- 66% from Russia: Russia is also a prominent player in the cyber threat arena, with 66% of organisations reporting attacks originating in the country. The diversity and sophistication of these attacks underscore the need for robust cybersecurity measures.
- 82% Increase in Russian Attacks: The data reveals a disconcerting trend – malicious automated attacks from Russia have surged by 82% in just two years. These attacks now account for over three-quarters of all attack traffic from Europe.
- 11% Increase Post-Sanctions: Russian-sourced cyberattacks have experienced an 11% increase since sanctions were imposed in early 2022. This suggests that punitive measures have not deterred cyber threat actors from the region.
- 72% of Gaming and Streaming Businesses Affected: The gaming and online streaming sector is particularly vulnerable, with 72% of businesses reporting cyberattacks originating in Russia. These attacks disrupt services and undermine user trust.
- Vietnam’s Surprising Role: Vietnam emerges as a notable outlier, ranking as the third-highest country of origin for cyberattacks. Astonishingly, 48% of organisations have reported attacks originating from Vietnam, despite the country accounting for just 2% of the population of Asia.
Global Cyber Threats: Russia And China At The Center
While attributing specific threat actors and motivations remains challenging, the data underscores the significance of Russia and China in cyber threat origination.
Key Insights:
- Over Half Affected: More than 50% of survey respondents reported experiencing cyberattacks originating from Russia or China.
- Massive Volumes of Automated Traffic: Notably, the data reveals that vast volumes of malicious automated traffic emanate from infrastructure located in Russia and China.
- Alignment with Prior Statements: These findings echo concerns previously raised by law enforcement and intelligence organisations in the United States. The FBI, for instance, has highlighted instances of ‘Chinese Economic Espionage’ on a large scale.
Attack Trends
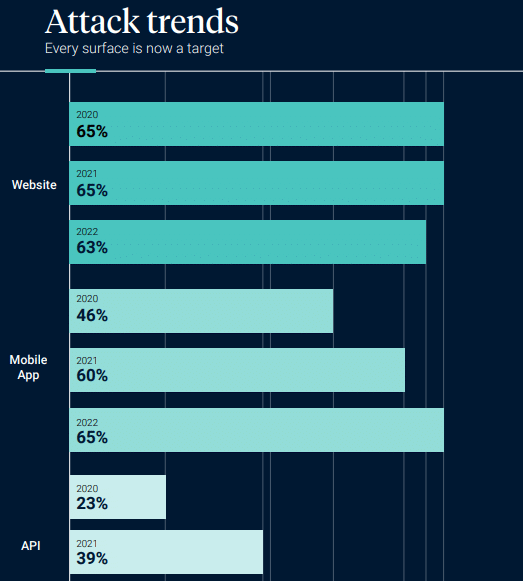
In the past year, a staggering 65% of cyberattacks have been directed at mobile devices, highlighting the growing vulnerability of mobile platforms.
Websites continue to be a prime target, with 63% of attacks focusing on compromising website security, while 40% of all attacks concentrate on exploiting vulnerabilities within APIs.
A significant milestone was reached in 2022 when cyberattacks on mobile applications surpassed those on websites for the first time, signifying a notable shift in attack vectors.
Bad Bots Cause Financial Harm to 81% of Businesses
Startling data points to a growing recognition of the harm inflicted by malicious bots, with a staggering 81% of businesses acknowledging financial repercussions. This represents a 47% increase compared to the previous year.
To grasp the magnitude of this impact, businesses have delved into the numbers, revealing that automated attacks exact an average toll of 4.3% of online revenues. To provide context for this financial burden, it’s crucial to understand the sheer scale of cumulative impact.
With average online revenues hovering around $1.9 billion, every company estimates it loses a substantial $85.6 million annually to bot-driven activities.
Bot-Induced Financial Damage: A Closer Look at Affected Business Sectors
The relentless and enduring presence of malicious automation on the web’s attack surface has cast a dark shadow on businesses, leading to substantial financial losses over time. The data underscores the diverse range of industries impacted by these harmful practices.
Key Insights:
Sniping:
- Among the highest-turnover companies surveyed, 9% reported that sniping attacks inflicted financial losses exceeding $260 million on their online revenues annually.
Scalping:
- 45% of companies with substantial online revenues, around $2.6 billion, stated that scalping attacks accounted for more than 5% of their online revenue losses.
Scraping:
- 30% of companies with online turnovers exceeding $2.6 billion indicated that scraping attacks led to losses exceeding 5% of their online revenues.
Credential Stuffing:
- A striking 2% of security leaders at the highest-turnover organizations disclosed that credential stuffing attacks resulted in losses exceeding 10% of their online revenues.
Fake Account Creation:
- Over 25% of smaller organizations, with an online run rate just above $100 million, reported losses of at least $6.2 million annually due to fake account creation.
Gift Card Fraud:
- An alarming 38% of organizations with total revenues exceeding $5 billion reported that gift card fraud cost them more than 5% of their total online revenues, equating to at least $130 million.
These findings underscore the significant financial burden placed on businesses across various sectors by malicious automation.
Customer Satisfaction at Risk: Malicious Automation Damages Company Reputations
Beyond the financial implications, data indicates that malicious automation is eroding companies’ standing with their customers. These findings reveal a concerning trend in customer satisfaction.
On average, a substantial 88% of surveyed businesses have reported that they’ve felt the adverse effects of bots on customer satisfaction. Even more concerning, 22% of these companies have witnessed a noteworthy decline of 6% or more in customer satisfaction directly attributed to the presence of malicious automation.

Principal Security Researcher at Netacea Cyril Noel-Tagoe says given the media’s interest in scalper bots and a high-profile appearance in Congress following the commotion surrounding the Taylor Swift Eras tour ticket release, it is perhaps no surprise that 93% of businesses identified scalping as a drain on reputation, the most impactful attack type.
“This was followed closely by credential stuffing – which can be a particularly ‘noisy’ attack for users, either locking them out after multiple failed attempts or forcing them to take arduous
remediation actions,” Noel-Tagoe said.
Gaps In Detection & Response
The cybersecurity landscape is fraught with challenges, and recent data reveals alarming gaps in the detection and response to cyberattacks. Businesses are taking significant time to realize the presence of various threats, leaving them vulnerable for extended periods.
According to data, the average length of time before detecting and responding to different cyber-attack types is as follows:
- Scalper: Businesses take an average of 3.44 months to detect and respond to scalping attacks.
- Sniper: Sniper attacks have an average detection and response time of 3.88 months.
- Account Checker: Companies require an average of 3.93 months to identify and address account checking attacks.
- Scraper: Scraper attacks go undetected for an average of 4.02 months before a response is initiated.
- Fake Account Creation: Detecting and responding to fake account creation attacks takes an average of 3.97 months.
- Gift Card Cracking: Businesses take an average of 3.40 months to detect and respond to gift card cracking attacks.
These statistics shed light on the critical need for businesses to enhance their cybersecurity practices and reduce the time it takes to detect and respond to cyber threats. The longer these threats go unnoticed, the greater the potential for financial losses and reputational damage.
The findings highlight poor detection times across the board, likely contributing significantly to the attritive business impact of malicious automation. Worryingly, the speed of detection and remediation times is measured in months, not days or weeks.
In fact, the research reveals that the average dwell time for a malicious automated attack on the web attack surface is 4 months. Nearly every single organisation researched, a staggering 97%, stated that it takes over a month to respond to malicious automated attacks.
This stark contrast with accepted best practices in detecting attacks in other areas of the technical environment is a cause for concern. For example, Mandiant’s recent M-Trends report indicates that average global dwell times have decreased to just 16 days.
Similarly, IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach report emphasises that breaches identified within 200 days are 26.5% less costly than breaches with a lifecycle greater than 200 days.
Urgent Call to Action: Addressing the Rampant Financial Damage Caused by Malicious Automation
This issue, as substantiated by the research, demands a prominent place in board-level discussions alongside the well-recognized threats of ransomware attacks and data breaches.
The incremental nature of financial, reputational, and operational costs, which permeates across various departments, often conceals the true impact within the numbers.
To effectively combat this pervasive problem, security leaders must establish a direct link between attack data and its tangible business impact.
By doing so, they can prevent malicious automation from being buried in the overall cost of conducting business. Only through this approach can they garner the essential support and resources from the C-suite to effectively address the issue.
Securing adequate resources is paramount in confronting the escalating threat posed by malicious automation. Attackers are exploiting an ever-expanding web attack surface, while the increasing sophistication of AI presents ample opportunities for attackers to amplify the volume and complexity of their assaults.
Furthermore, the reluctance of regulators in Western nations to act, coupled with the presence of malevolent infrastructure in countries with contrasting worldviews, presents a broader challenge.
Without sufficiently intelligent AI-driven defenses in place, companies risk becoming complacent about the accelerating damage caused by malicious automation, ultimately impacting their bottom line.
This complacency is a costly lesson for those who invest in inferior solutions. Encouragingly, Gartner has recently highlighted that this market is poised to mature over the next two years, driven by several factors outlined above.
The onus for action squarely rests on the shoulders of security leaders, who must begin by acknowledging the magnitude of this problem. Without this acknowledgment, companies will continue to suffer a slow erosion, facing the cumulative impact of malicious automation







