Big Data has been in the news lately, not least because of its potential to transform businesses by allowing companies to analyse massive amounts of data. Some see Big Data as a danger to traditional business, others see it as a potential tool for great value.
What must be understood is that there are different kinds of Big Data. While some forms of Big Data are beneficial, others can be dangerous if not properly managed.
Big data refers to the ability to extract insights from huge amounts of structured data quickly, easily, and economically. Big data has also led to much progress in computer science, especially in the area of big data mining.
The term “big data” is now a popular one, but this term is actually a misnomer. There is no such thing as “big data”. The phrase is often used to describe some new development in data mining or artificial intelligence.
Big data has also been transforming business practices for at least the last three decades. Prior to that time, business decision makers were limited in their capacity to apply certain business practices to their data or to extract insights from it that would help them make better decisions.
Today, the ability to use big data techniques and concepts is at the core of most every successful company. Companies across all industries are harnessing the power of big data in their efforts to remain competitive and ultimately succeed. One common thread running through all of these businesses is the desire to leverage big data to drive business value and increase company competitiveness.
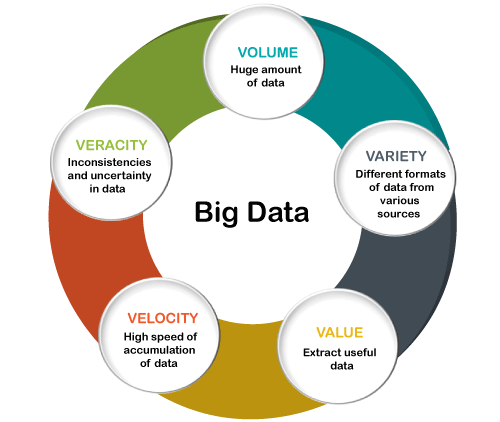
Big data comes in many forms. Some examples include text, images, videos, maps, audio, social networks, web feeds, mashups, and much more. While each of these can be useful in certain circumstances, there are common denominators which allow for the extraction of large amounts of data from diverse sources.
The inherent potential to extract value from big data workloads is truly at the heart of many of today’s advanced technologies. In this article we will discuss some of these potential applications and the impact they have on companies.
When considering the possibilities in big data, it is not only the potential to extract value from existing data that excites many. It is also the potential to make inferences from such data that can inform and perhaps even predict future behavior.
One example of using customer data to predict customer preferences is what is known as social media analytics. This form of analytics begins by gathering basic information about a user’s behavior on various social media channels such as Facebook and Twitter.
Structured Data
This is the backbone of the internet and much of corporate IT. Structured data allows users to gain insight into complex business patterns by creating relationships from large amounts of normally distributed, unstructured data.
Examples include sales patterns, customer behavior, and demand trends. With the correct tools and training, data mining can allow analysts to identify profitable relationships within organisations and create new products and services on the fly.
Social Media Data Mining
With social media and more specifically sites such as Twitter and Facebook being used by millions of people around the world, big data analytics is necessary for marketers and businesses to get a full picture of consumer behavior.
Examples include how the use of Twitter or Facebook can help companies increase product awareness, generate leads, and track campaign effectiveness. Twitter in particular has been used for lead generation by political candidates and brands. In fact, this kind of marketing analytics was recently showcased at the Boston Web Festival where top businesses in the area were able to use it to win over voters.
Big Data Analytics
Moving pieces of information through systems such as Big Data analytics is one of the most basic forms of big data. It enables analysts to explore relationships through a network of moving parts.
For example, this can be used to discover what customer interactions with a given brand or company have been over a given period of time. As a result, a business owner can determine whether or not the customer experience has been an effective measure of that brand’s or company’s success.
Big data analytics is just beginning to blossom in the realm of consumer and enterprise applications. The best place to learn more about the exciting future of advanced analytics is to visit cloud-based analytics integrators.
These specialists will consult with you and develop a custom solution tailored to your organisation. Whether you need metrics to gauge ROI or want to explore the mysteries of human behavior, cloud-based solutions are the ideal way to get the job done.
The emerging discipline of Big Data analytics challenges traditional business processes by tapping into the significant amount of information already available in the external environment.
These processes may include weather, supply chain, travel, consumer behavior, natural disasters, telecommunications, entertainment and location-based services such as car rentals and hotel reservations.
The information can then be processed into business intelligence or decision making tools that are then used for specific purposes such as fraud management, customer service, product and service analysis, internet marketing, telematics, and online gaming.
Businesses that lacking in the required experience and expertise in large scale data processing cannot effectively leverage the complex capabilities of advanced technologies. Therefore, the need for professionals who have the skills, experience and tools necessary to rapidly and efficiently process the huge volume of data available today is of great importance.
Predictive Analytics
Most of the time, marketing strategies are formulated with the data mined in order to provide insights that will either support or contradict a given idea. However, predictive analytics takes this notion to a higher level by using it to forecast future results. This is often used by companies in order to create marketing campaigns.
In fact, Google forecasted that over the next year, over forty percent of their ad dollars would be directed towards paid advertising. While this concept seems far fetched, many marketing firms have used predictive analytics to generate lucrative ad campaigns.
Customer Service Analytics
Similar to predictive analytics is customer service analytics. These two customer data types are often used interchangeably, but there are distinctions. Customer service analytics takes into consideration factors such as customer satisfaction and interaction rates.
It also takes into account the types of questions customers ask, the length of time they spend on a particular website, and the number of return/satisfied customers.
While both customer data types provide insight into customer satisfaction rates, customer service analytics focuses more on the actual actions that customers take such as purchasing decisions and the amount of time they spend on a particular website.
Analytics Tools
Big Data analytics tools are a great way for today’s marketing strategies to make better decisions and provide better insights into customer behavior. Businesses must find a balance between indulging in Big Data and making better decisions based on current information. A balance of Big Data and traditional analytics tools will most likely provide the best results.
Security
One of the primary questions that arises is how to manage and analyse big data. When large amounts of data are stored, it becomes a challenge to safely store the data, as it can be subject to malicious attacks from hackers and others who may try to misuse the structured data. Additionally, if the data is not organised in a meaningful way, it can become difficult to search for specific information.
Another concern is the potential misuse of the data. For example, many criminals have developed means of manipulating databases by using known names, where real people may have been unidentified. It is also not uncommon for criminals to use fake person data to create a massive onslaught of spam or otherwise destructive internet activity.
By means of big data analytics, organisations can detect suspicious activity that could lead to infiltration of their networks. There are two primary ways this can occur: human or automated. Human-based activities include such things as social network usage, use of electronic mail, and travel, while automating activities include data breaches stemming from hacking, malicious software, and fraudulent transactions.
All of these pose a risk to an organisation’s confidential information and often require some level of training for employees to be aware of how to deal with potential risks. With all of the potential risks, it’s important that organisations can detect and report suspicious activity promptly so that security can be increased without sacrificing time or productivity.
Data Velocity
Data velocity describes the rate at which information is created, analysed and distributed. The velocity rate tends to vary according to factors like the number of people using the internet and the number of sensors installed on IoT enabled devices.
This is also dependent on factors like the age of the device and its usability. Another important factor for defining velocity is the purpose of the analysis or report that is being created.
Cloud Based Analytics
Cloud-based analytics is a term that has recently been gaining a lot of popularity in the business domain. Cloud computing offers an apt platform for big data analysis owing to the high storage and computing needs of both the former.
This makes cloud-based analytic a very viable field. But, many challenges have to be faced and potential benefits need to evaluate before such potentially useful applications of the synergistic model could be widely used. This article will briefly discuss some of these challenges and the ensuing steps that need to be followed for successful use of such tools.
Cloud-based big data analytics comes with the potential to bring numerous advantages to any organisation. It is primarily because of this potential that cloud computing has been considered as the most apt medium for data mining. The main advantage of using this medium is the reduced costs of implementing the same.
Here Are 10 Big Data Statistics
- Data Growth: Over 2.5 quintillion bytes of data are generated every day, and it’s estimated that 90% of the world’s data has been created in the last two years alone.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Impact: By 2025, it’s projected that there will be over 75 billion connected IoT devices, contributing significantly to the big data ecosystem.
- Social Media Data: Facebook alone generates more than 4 petabytes of user data every day, including posts, images, videos, and interactions.
- Global Data Economy: The global big data market size is expected to reach $229.4 billion by 2026, driven by the increasing adoption of analytics, AI, and cloud technologies.
- Real-time Processing: In industries like finance and e-commerce, real-time data processing is critical. Some platforms process millions of events per second to make instant decisions.
- Unstructured Data Dominance: Unstructured data, such as text, images, and videos, accounts for around 80-90% of the data generated today, presenting challenges and opportunities for analysis.
- Machine Learning Integration: Machine learning and AI algorithms are being integrated into big data platforms to uncover insights and patterns that would be impossible or time-consuming for humans to discover.
- Data Privacy Concerns: With the increase in data breaches and privacy concerns, regulations like GDPR and CCPA are reshaping how organizations handle and protect customer data.
- Cloud Adoption: Cloud computing has accelerated big data adoption. Over 90% of organizations use cloud services for data storage, processing, and analytics.
- Data Science Skills Demand: The demand for data scientists and analysts is rising rapidly. By 2025, the number of data science job openings is expected to exceed 800,000.
These statistics highlight the immense impact and growth of big data in various sectors, from business and technology to healthcare and beyond.
As the volume and variety of data continue to expand, the ability to effectively manage, analyze, and derive insights from big data becomes increasingly important.
Deep Learning
Another way to analyse large amounts of structured data is through the use of deep learning. Deep learning refers to the process of using mathematical programming to form networks. The networks formed are then used to make inferences from the data that was analyzed.
Deep learning analytics is very similar to traditional data mining, but the approach is much more targeted because it is trained on incredibly large databases.
Deep learning applications can also be used for things like product cataloguing, online behaviour analysis, customer self-service management and image recognition. The accuracy of these applications is currently measured in terms of millions of accurate calls made by humans as a result of the analytics tool being used.
Big Data: Transforming Industries and Shaping the Future
In an age where information is generated at an unprecedented pace, businesses, governments, and individuals are harnessing this torrent of data to uncover insights that were once thought to be beyond the realm of possibility. As we stand at the crossroads of technology and information, the impact of Big Data on industries and society at large is undeniable.
- Unprecedented Growth and Potential
Recent statistics show that data creation has reached astonishing levels, with over 2.5 quintillion bytes of data being generated daily.
This colossal volume, an outcome of digitalization and connectivity, has given birth to new opportunities and challenges that are reshaping traditional paradigms across sectors. From healthcare and finance to retail and manufacturing, Big Data’s transformative influence is pervasive.
- Driving Innovation Across Sectors
In healthcare, Big Data is revolutionising patient care, diagnosis, and drug development. Through the analysis of medical records, genomics, and patient outcomes, doctors and researchers are making more accurate predictions and personalizing treatments.
Financial institutions are leveraging data-driven insights to combat fraud, optimize trading strategies, and enhance customer experiences. Even the realm of agriculture has not been left untouched, as farmers utilize data-driven insights to optimize crop yields, conserve resources, and promote sustainable practices.
- From Descriptive to Predictive Insights
Traditional data analysis was primarily descriptive – it explained what had happened in the past. Big Data, however, has taken analytics to the next level. With advanced algorithms and machine learning, organizations can now predict future trends, behaviors, and outcomes.
Imagine predicting disease outbreaks before they happen, adjusting supply chains in real-time based on demand projections, and even preventing equipment failures before they occur. These possibilities are no longer science fiction but a tangible reality.
- The Challenge of Responsible Data Usage
While Big Data’s potential for good is immense, its ethical and privacy implications cannot be overlooked. The vast amount of personal information being collected raises concerns about data privacy and security.
Regulations like GDPR and CCPA are designed to ensure responsible data usage, putting the onus on organizations to handle data transparently and securely.
- Charting the Future
As the trajectory of Big Data continues to rise, so too does the demand for skilled professionals who can navigate its intricacies. Data scientists, analysts, and engineers are now at the forefront of innovation, armed with tools that can turn raw data into actionable insights.
Governments, industries, and academia are collaborating to equip the workforce with the necessary skills to thrive in this data-driven landscape.
Extended Summary
The emerging discipline of Big Data delves deep into the technological, economic and sociological impacts of this extraordinary amount of data. Companies are leveraging this powerful technology to support multiple business functions by deploying data management systems, data warehouses, and advanced Big Data technologies.
They are using these tools to analyse and interpret big data, generate and manage visual intelligence, and extend and deliver analytical software. Organisations need to deploy enterprise software solutions that encompass both the conceptualisation of big data as well as the practical implementation of it
The power of big data analytics lies in the ability of having insights into the past and present actions of customers. With the help of big data technologies, marketers can now get a clear insight into the buying behaviors of their customers even after just a few days of usage.







