As reliance on artificial intelligence (AI) grows across various sectors, from customer service to operational streamlining, a darker side of AI emerges: its potential to facilitate cyber threats.
The magnitude of the threat is evident. Almost half (46%) of cybersecurity professionals anticipate that AI will heighten companies’ vulnerability levels.
Meanwhile, ransomware has surged as a primary concern, with 62% of survey participants indicating it as the foremost worry for their executive leadership, marking a 44% increase from just a year ago.
Recent findings indicate a concerning trend where threat actors exploit AI for malicious purposes, amplifying the scale and impact of cyber attacks.
Cybercriminals are increasingly weaponizing Artificial Intelligence (AI) to execute more sophisticated, large-scale, and advanced targeted cyberattacks. AI has empowered these attackers to develop adaptive malware that evades detection, craft highly convincing phishing schemes, and automate complex assaults.
Ways AI Empowers Cyber Attacks
- Crafting hyper-realistic phishing campaigns and personalized social engineering traps.
- Swiftly analysing networks and applications to identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Producing malicious code and malware engineered to bypass conventional defenses.
- Automating various stages of an attack to increase efficiency and effectiveness.
- Handling stolen data and executing attacks more swiftly than human hackers.
How Is AI Used In Cyber Attacks?
Cyber criminals may use AI to: Easily create new malware that can contain new zero-day vulnerabilities or bypass detection. Create new, sophisticated, original, or targeted phishing attacks. Such actions can increase the number of scenarios, making it difficult for reputation engines to keep up.
Example Of An AI Powered Attack?
One common type is the use of AI to generate convincing phishing emails. Threat actors leverage AI-powered models and language generation techniques to craft emails that appear legitimate and deceive recipients into revealing sensitive information or performing malicious actions.
AI: DDoS Attacks
In the first half of 2023, a staggering 7.9 million Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks were recorded worldwide, averaging a shocking 44,000 attacks per day,
This marks a staggering 31% increase compared to the same period in 2022, showcasing the growing efficacy of AI-enabled attacks.
The National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) underscores this threat in its latest report, predicting a surge in both the frequency and impact of cyber attacks over the next two years, driven by the widespread adoption of AI among threat actors.
The Dark Side of AI: How AI Is Escalating Cyber Attacks
In recent years, the remarkable strides made in Artificial Intelligence (AI) have yielded numerous positive impacts across various facets of life.
From the deployment of self-driving cars, which have contributed to a decrease in automobile accidents, to the proliferation of virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa, aiding individuals in organisation, and even tools like ChatGPT, enhancing productivity for professionals and students alike, the capabilities of AI have exceeded expectations.
Nevertheless, this progress prompts contemplation on the potential for AI to be exploited, leading to an exploration of its darker implications where millions of cybercriminals leverage its capabilities for nefarious purposes.
In 2017, the global damages inflicted by cyber crimes amounted to just over $1 trillion USD. However, by 2022, this figure ballooned to over $10 trillion USD, marking a tenfold increase in damages within a mere five-year span.
Evidently, cyber attacks are proliferating at an alarming rate, prompting the question: what factors contribute to this concerning trend?
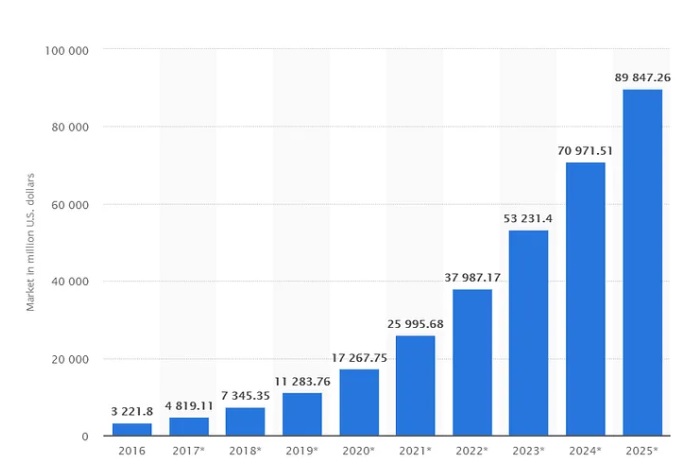
AI stands as the fastest-growing technology globally. The graph below shows the exponential growth of the AI industry market size each year, with projections indicating a continued upward, exponential trajectory.
The Growth Trajectory of the AI Industry Market Size (2016–2025) in US Million Dollars
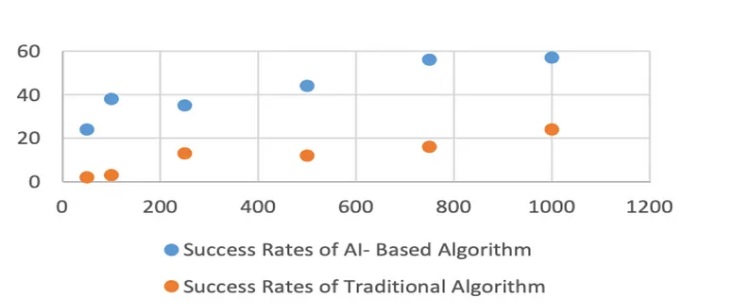
AI Powered Cyber Attacks – Password Cracking
Cybercriminals are increasingly utilizing AI to enhance their ability to crack users’ passwords. Conventionally, hackers relied on brute force algorithms, systematically testing passwords until discovering the correct one.
However, a recent trend involves employing AI models to swiftly identify and test the most commonly used passwords, resulting in a higher success rate.
A study examined and compared the success rates of AI-driven and traditional brute-force attacks across various dictionary lengths, representing the number of words or terms in the potential password set: 50, 100, 250, 500, 750, and 1000 words.
The study aggregated results from 100 trials for each dictionary length. The graph below illustrates the study’s findings, clearly demonstrating the superior effectiveness of AI-based algorithms over traditional methods in password cracking.
The following graph illustrates the study’s findings, clearly demonstrating the superior effectiveness of AI-based algorithms over traditional methods in password cracking.
The Cyber-Physical Attack
When discussions turn to cybersecurity breaches, many conjure images of frozen screens, ransomware demands, and disruptive DDoS attacks that disrupt connectivity for hours, if not days.
However, some experts are expressing concern over the emergence of what they term “cyber-physical attacks,” particularly with the widespread adoption of artificial intelligence by hackers, be they individuals or nation-states.
Highlighting this concern, the FBI recently briefed Congress on the infiltration of American cyber infrastructure by Chinese hackers, warning of potential severe consequences.
FBI Director Christopher Wray disclosed that Chinese government-backed hackers have targeted essential systems such as water treatment facilities, the power grid, transportation networks, and other critical infrastructure within the United States.
Stuart Madnick, an MIT professor of engineering systems and co-founder of Cybersecurity at MIT Sloan (CAMS), has studied and written about the cyber-physical nexus.
He said with the widespread arrival of generative AI, concerns about physical attacks being the next phase of cybercrime have grown.
Combatting The Artificial Intelligence Threat
State and non-state actors, both skilled and less proficient, are increasingly leveraging AI to enhance their cyber capabilities, posing a significant challenge to cybersecurity efforts globally.
Of particular concern is the expected rise in ransomware attacks facilitated by AI, as cyber criminals capitalise on the accessibility and sophistication of AI-driven tools.
The evolution in cyber threats necessitates a proactive approach to defense, as traditional security measures struggle to keep pace with the evolving threat landscape.
Fortunately, businesses can harness AI themselves to bolster their defense mechanisms. By leveraging AI-driven threat intelligence, organisations can swiftly identify and mitigate emerging threats, enhancing their resilience against cyber attacks.
Additionally, AI-integrated cybersecurity solutions offer real-time monitoring and response capabilities, enabling organizations to adapt to evolving threats dynamically.
From automated threat detection to natural language processing (NLP) for phishing detection, AI empowers organizations to fortify their cybersecurity posture amidst escalating cyber threats.
As cyber attacks grow in frequency and complexity, the strategic deployment of AI-driven defenses becomes imperative for organisations seeking to safeguard their digital assets effectively.
- Countering AI-Driven Cyberattacks With AI-Driven Cybersecurity
Threat actors are rapidly embracing emerging technologies, particularly artificial intelligence, to enhance their effectiveness in targeting victims.
In 2021, during the Colonial Pipeline attack, cybersecurity incidents led to a successful breach 18% of the time, as reported by the Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report. Since then, the success rate has surged to over 30%.
As threat actors leverage AI to bolster their capabilities, it is imperative for organizations worldwide to evolve in parallel, not only to react to these threats but also to proactively thwart them.
According to KnowBe4, at least 70% of malicious breaches stem from social engineering or phishing attacks. That means that attackers don’t necessarily exploit a technical vulnerability at all, but instead persuade users to surrender their legitimate access credentials, This attack vector has only gotten more dangerous following the debut of generative AI models in 2022.
In recent years, a surge in cyberattacks has targeted a wide array of institutions, from multinational corporations to local schools and healthcare facilities.
Reports reveal a startling trend, with healthcare organizations alone facing a staggering 1,634 cyberattacks per week in the first half of 2023, marking an 18% increase compared to the previous year.
The financial repercussions of these attacks are profound and diverse, ranging from ransom demands to the exposure of sensitive data and the disruption of essential services.
Lawsuits following breaches have resulted in settlements reaching hundreds of millions of dollars, prompting a seismic shift in the insurance industry. Insurance premiums have skyrocketed, rendering coverage prohibitively expensive for many organizations.
Recogniaing the escalating threat landscape, organisations are turning to defensive AI as an essential tool in their cybersecurity arsenal. Even well-funded entities acknowledge the need for a force multiplier to combat modern threats effectively.
Defensive AI provides a crucial foundation for organisations of all sizes, offering proactive detection and remediation capabilities to thwart attacks and mitigate risks.
Moreover, the proliferation of new technologies, particularly Internet of Things (IoT) devices, has created new avenues for cybercriminals to exploit. As malicious actors increasingly leverage AI in their attacks, organizations must deploy AI-driven defenses to counter these evolving threats.
To address these challenges, experts advocate for the adoption of consolidated cybersecurity platforms leveraging AI technologies. Such platforms provide comprehensive protection, identifying abnormal behavior and enforcing stringent security policies to enhance resilience against a broad spectrum of cyber threats.
Prevention-focused cybersecurity, empowered by AI solutions, is attainable for organisations across industries. Establishing a unified security posture fortified by AI represents the next frontier in cybersecurity protection.
AI-Powered Cyber Attack Tools – What Could Be Used?
AI-powered cyber attack tools, if they existed, could potentially leverage various techniques and technologies to enhance their effectiveness in carrying out malicious activities. Here are some hypothetical ways in which AI could be utilized in cyber attacks:
- Automated Exploitation: AI could be used to automatically identify and exploit vulnerabilities in software systems or networks. This could involve scanning for weaknesses and launching attacks without human intervention.
- Adversarial Machine Learning: Attackers could use AI to generate sophisticated adversarial examples to bypass security mechanisms such as intrusion detection systems or spam filters. Adversarial machine learning techniques could be employed to craft malicious inputs that appear benign to traditional security defenses.
- Dynamic Malware Generation: AI algorithms could be used to automatically generate polymorphic or metamorphic malware that constantly evolves to evade detection by antivirus software and other security controls.
- Social Engineering: AI-powered chatbots or conversational agents could be used to conduct more convincing social engineering attacks by engaging in realistic conversations with victims to trick them into disclosing sensitive information or performing actions that compromise security.
- Automated Phishing Campaigns: AI could be used to personalize phishing emails at scale by analyzing data on potential victims to craft messages that are more convincing and likely to result in successful compromises.
- Autonomous Botnets: AI algorithms could be used to autonomously control botnets, optimizing their behavior and coordination to carry out large-scale distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks or other malicious activities.
- Automated Reconnaissance: AI-powered tools could automate the process of gathering information about potential targets, such as scanning websites, social media profiles, or publicly available databases to identify vulnerabilities or gather intelligence for targeted attacks.
Examples Of AI-Powered Cyber Security Tools
- The decision, set to take effect on April 22, has left many free users disgruntled, questioning the platform’s commitment to accessibility in SEO analytics.
- Network Detection and Response (Darktrace, Vectra AI etc.): Leading AI cybersecurity companies that provide enterprise-wide threat detection and response.
- Endpoint/Extended Detection and Response (SentinelOne, BlackBerry Cylance etc.): Provides AI-powered endpoint security for cloud, container, and IoT devices, offering autonomous cybersecurity defense.
- User and Entity Behaviour Analytics (Exabeam, Cybereason etc.): Utilizes AI hunting, behavioral analysis, and automated response to detect and respond to cyber threats.
- Security Information and Event Management (Splunk, Elastic, …): AI learns about logs within the organisation and can be searched with natural language via Generative AI.
- Security Orchestration Automation Response (Swimlane, Microsoft Sentinel etc.): Provides AI powered automated incident response e.g. executing use cases or getting done defined processes.
Cybersecurity Leaders Say Recent Attacks Powered by AI
Seventy-five percent of security professionals said they have seen an uptick in attacks over the past year, with 85% attributing the rise to bad actors using generative AI
Among security professionals who have seen upticks in cybercrime, a majority attribute the rise to bad actors using generative AI.
Chief Financial Officers (CFOs) are being urged to adopt innovative tools like generative AI. However, alongside the potential benefits, there’s a growing concern among industry leaders about the cybersecurity risks associated with the integration of these technologies.
According to a recent report by Sapio Research and Deep Instinct, which surveyed over 650 cybersecurity experts and leaders, there has been a notable surge in cyberattacks over the past year. A staggering 75% of respondents attributed this increase to malicious actors exploiting generative AI.
The report highlighted various concerns raised by cybersecurity professionals regarding AI’s role in cybersecurity threats. Nearly 39% expressed worries about heightened privacy concerns, while 37% feared a rise in undetectable phishing attacks.
Additionally, a third of respondents voiced concerns about the escalation in both the frequency and sophistication of cyber assaults, alongside the emergence of deep fakes being used to orchestrate these attacks.
Generative AI Can Create Vulnerabilities
Businesses are gearing up to integrate new technology driven by generative AI into their operations, but cybersecurity experts are cautioning that this move could inadvertently open up vulnerabilities to cyber threats.
According to a recent survey, nearly half of respondents (46%) expressed concerns that the adoption of generative AI could make their organizations more susceptible to cyber attacks compared to before the implementation of AI.
This heightened risk has prompted a shift in the cybersecurity landscape, with researchers advocating for a departure from traditional reactive approaches to a more proactive stance. Instead of merely responding to cyber threats as they arise, industry leaders emphasize the importance of fortifying data security measures beforehand.
The shift towards proactive strategies has gained significant traction, with a notable 95% increase in favorability towards this approach compared to the previous year (72% this year versus 37% last year).
When questioned about their primary concerns regarding AI’s impact on cybersecurity, respondents offered a range of perspectives. Thirty-nine percent expressed worries about heightened privacy issues, while 37% anticipated a rise in undetectable phishing attacks.
Additionally, a third of respondents foresaw an increase in both the frequency and speed of cyber attacks, along with a surge in the use of deep fakes to facilitate these malicious activities.
Cost Association
The surge in both the frequency and costs of cyber attacks is undoubtedly alarming, largely due to the apparent success of cyber criminals.
Recent findings reveal a concerning trend: a significant portion of respondents (47%) report that their companies now have a policy in place to acquiesce to any ransom demands stemming from cyber security threats. This marks a notable increase of 13% since the previous year.
Additionally, 42% of respondents admit to having paid for the return of stolen data within the past year, a stark comparison to the mere 32% reported in 2022.
Data also underscores a harsh reality: yielding to hackers’ demands does not ensure immunity from the ramifications of the attack. Shockingly, almost half (45%) of those who complied with cyber criminals’ demands still found their data exposed despite their cooperation.
Cyber Report Summary
While AI presents unprecedented opportunities for operational efficiency, its misuse by malicious actors and bad bots underscores the urgent need for robust cybersecurity measures.
As the battle between cyber defenders and threat actors intensifies, the strategic utilisation of AI emerges as a crucial determinant of cybersecurity resilience.
Artificial intelligence (AI) holds vast promise for enhancing various aspects of our world. However, there exists a shadowy dimension to AI, where its capabilities are exploited by countless cybercriminals on a daily basis.







